Getting Starting with Diamond Gradient Tool
Geometry Parameters
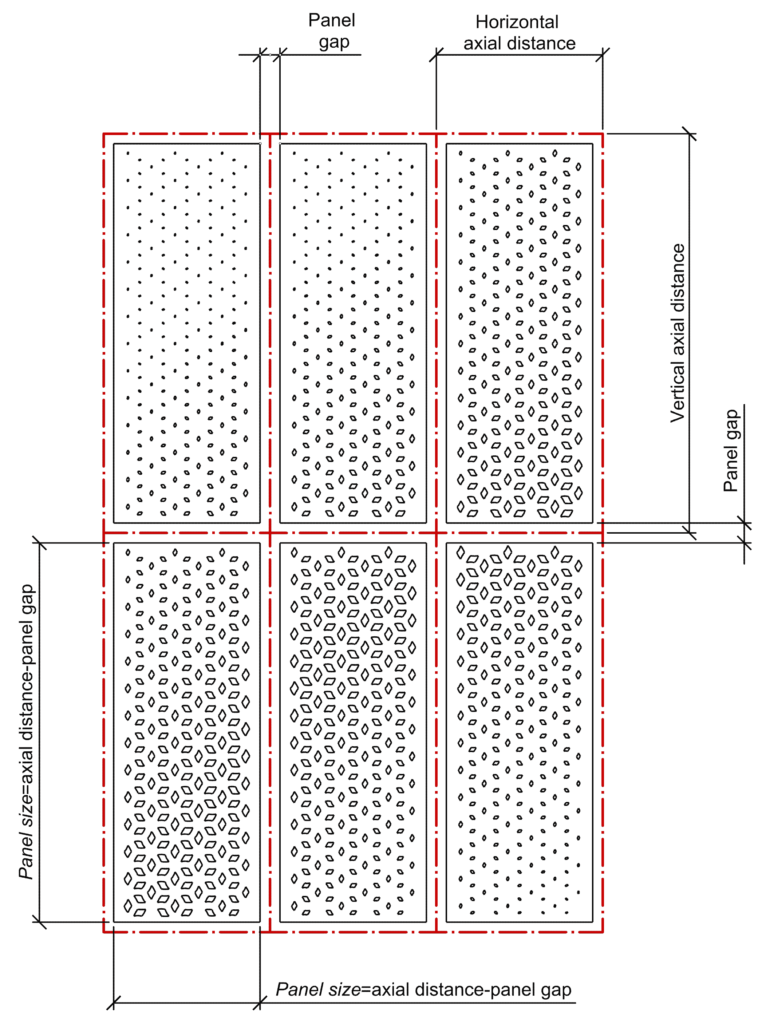
Panel settings:
Horizontal axial distance – the horizontal axial distance between two panels.
Vertical axial distance – the vertical axial distance between two panels.
Number of panels in X direction and Number of panels in Y direction – sets the number of panels.
Panel gap – determines the distance between adjacent panels. The size of the panel is subtraction of the axial distance and the panel gap.
Perforation settings:
Perforation density – adjusts the size of the perforations (higher density results in smaller openings).
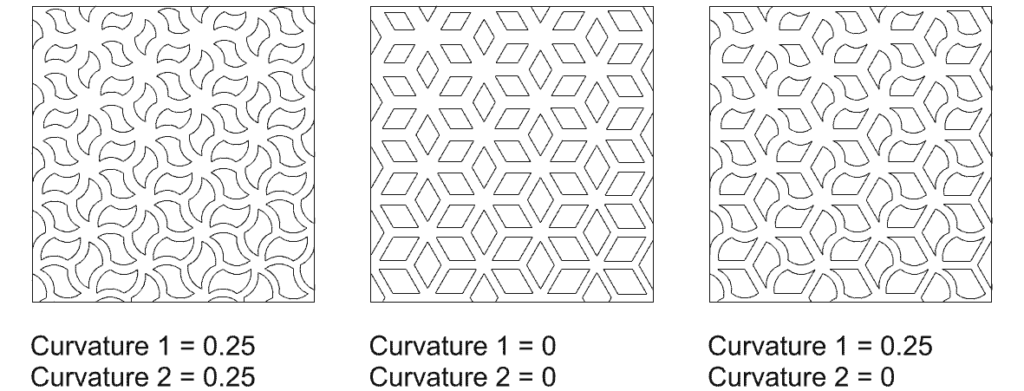
Curvature 1 and Curvature 2 – set the outline of the opening. A value of 0 results in a straight line, while higher values create curved outlines.
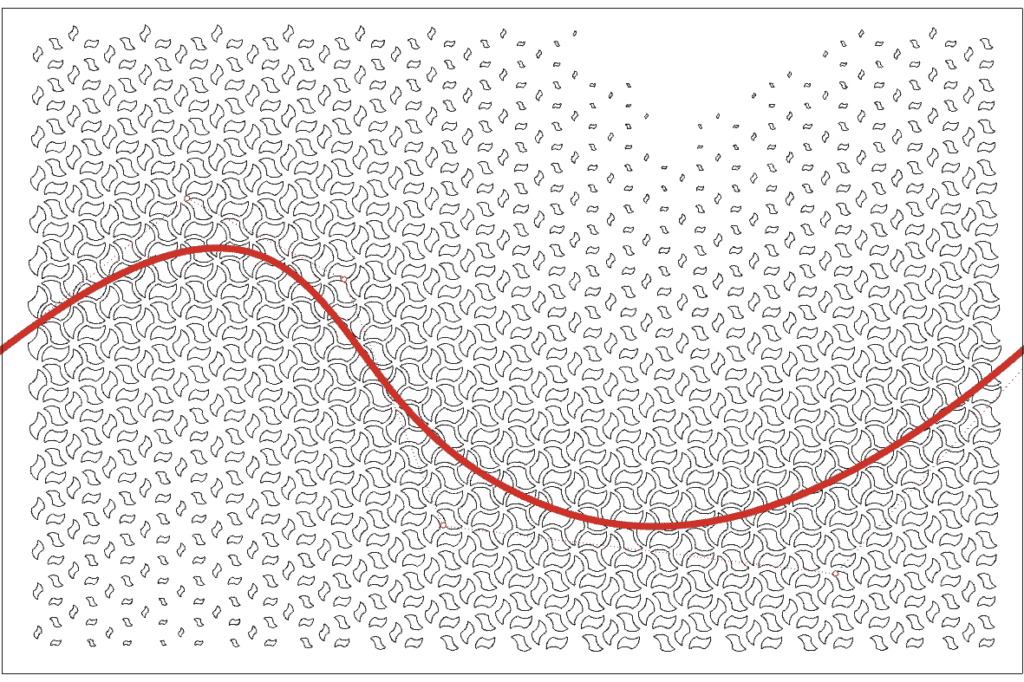
The distribution of perforations is controlled by the attractor, a curve that passes through marked points (green spheres). The largest/smallest openings will be along this curve. The attractor line can be adjusted by dragging and dropping points on the screen.
Attractor influence – determines whether the openings closest to the attractor curve will have the maximum or minimum size.
Falloff – controls how sharp or soft the transition between large and small holes is. A value of 1 creates the softest falloff, while 0 creates the sharpest falloff.
Remove smallest holes – additionally removes small holes.
Diamond Gradient Panel Materials
Color – sets the color of the tin. You can use the color picker or input RGB values.
Attractor visibility – shows or hides control points.
For more tutorials, check out our Tutorials page or subscribe to Spona YouTube channel for the latest updates.